CERIF (the Common European Research Information Format) is:
- A concept about research entities and their relationships – Specification (Conceptual Level)
- A description of research entities and their relationships – Model (Logical Level)
- A formalization of research entities and their relationships – Database Scripts (Physical Level)
Click on the image below to get an introductory presentation on CERIF (ppt).
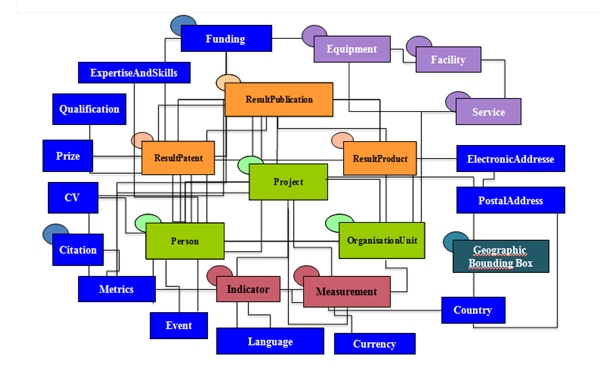
The data model (data-centric) allows for a (metadata) representation of research entities, their activities / interconnections (research) and their output (results) as well as high flexibility with formal (semantic) relationships, enables quality maintenance, archiving, access and interchange of research information and supports knowledge transfer to decision makers, for research evaluation, research managers, strategists, researchers, editors and the general public.
A CRIS can be implemented using a subset or superset of the full CERIF model for projects, people, organisations, publications, patents, products, services and facilities (equipment in particular) with role-based, temporally-bound relationships. The advantages of CERIF are: its neutral architecture; the data model can be implemented [relational, object-oriented, information retrieval (including WWW)]; the process model can be implemented [DBMS and query (centralised or distributed), HTML web / harvesting / IR-query, advanced knowledge-based technology].
But interoperation requires a structured schema. Today CERIF is used as a model for implementation of a standalone CRIS (but interoperation ready), as a model to define the wrapper around a legacy non-CERIF CRIS to allow homogeneous access to heterogeneous systems and as a definition of a data exchange format to create a common data warehouse from several CRIS.
After the hand-over of the custodianship of CERIF to euroCRIS in 2000 the original EU Working Group on Research Databases evolved into the very active euroCRIS CERIF Task Group, which has led CERIF through various upgrades and extensions. Ultimate aims of CERIF are to enable the ERA (European Research Area) e-infrastructurethrough standardization, integration and interchange and added-value services and to serve as middle (interoperability) layer for (EU) research information.